What Is Cloud Storage and How Does It Work?
What Is Cloud Storage and How Does It Work?
Cloud storage has become one of the most critical components of modern digital infrastructure. From individuals backing up personal photos to global enterprises managing petabytes of sensitive data, cloud storage solutions power today’s internet-driven economy. In Tier-1 countries such as the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, and across Europe, cloud storage adoption is accelerating due to scalability, security, and cost efficiency.
This comprehensive guide explains what cloud storage is, how it works, its underlying architecture, pricing models, security standards, and why it plays a central role in high-value industries like SaaS, finance, healthcare, cybersecurity, and enterprise IT—industries known for generating very high eCPM and CPC.
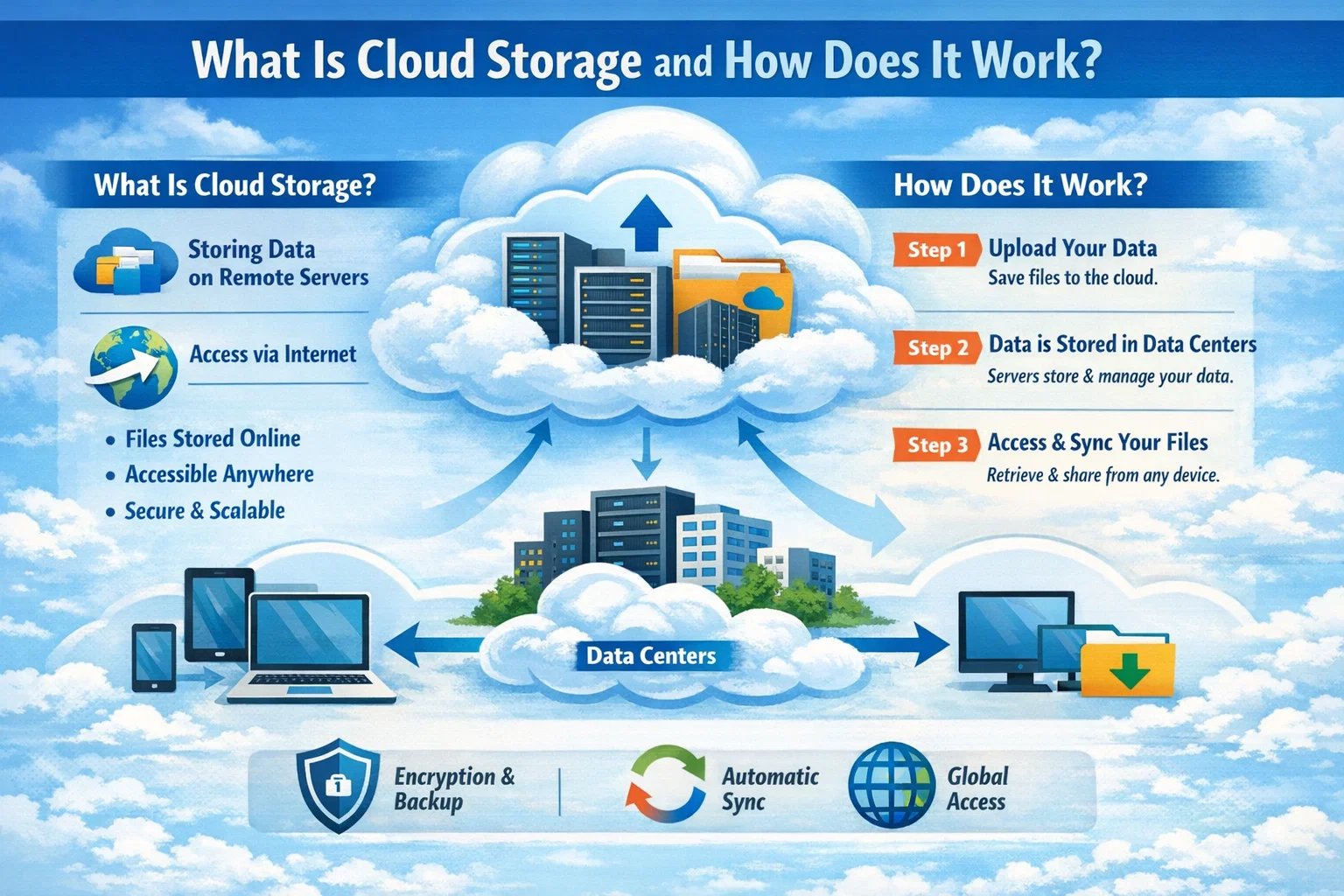
What Is Cloud Storage?
Cloud storage is a service model that allows data to be stored, managed, and accessed over the internet instead of on local hard drives or on-premise servers. The data is stored in remote data centers operated by cloud service providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and other enterprise-grade vendors.
Users can upload files, databases, backups, and application data to the cloud and access them from anywhere with an internet connection. This flexibility has made cloud storage the foundation of modern digital transformation strategies.
How Cloud Storage Works
At a technical level, cloud storage works by distributing data across multiple servers located in secure data centers. When a user uploads data, it is encrypted, replicated, and stored across different locations to ensure availability and durability.
The basic workflow includes:
- User uploads data via web app, API, or software client
- Data is encrypted in transit using secure protocols
- Data is stored across redundant storage nodes
- Metadata is indexed for fast retrieval
- Users access data on demand through authenticated requests
This architecture ensures high availability, fault tolerance, and performance—key requirements for enterprise workloads and cloud-native applications.
Types of Cloud Storage
Cloud storage services are generally categorized into three main types, each designed for specific use cases and performance requirements.
1. Object Storage
Object storage is the most common cloud storage model. Data is stored as objects with unique identifiers and metadata. It is ideal for unstructured data such as images, videos, backups, and application assets.
Popular use cases include media hosting, SaaS platforms, data lakes, and backup solutions.
2. Block Storage
Block storage divides data into fixed-size blocks and is typically used for high-performance workloads such as databases and enterprise applications.
This type of storage is common in financial systems, ERP platforms, and mission-critical SaaS products.
3. File Storage
File storage organizes data in a hierarchical file system, similar to traditional network drives. It is often used for shared file access and collaboration.
Public, Private, and Hybrid Cloud Storage
| Cloud Model | Description | Best For | Cost Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Cloud | Shared infrastructure managed by provider | Startups & SaaS | High |
| Private Cloud | Dedicated infrastructure | Finance & Healthcare | Medium |
| Hybrid Cloud | Combination of public & private | Large enterprises | High |
Why Businesses Use Cloud Storage
Businesses in Tier-1 economies rely on cloud storage for several strategic reasons. The ability to scale instantly, reduce infrastructure costs, and ensure data security has made cloud storage a default choice.
- Elastic scalability without upfront hardware investment
- Pay-as-you-go pricing models
- Enterprise-grade security and compliance
- Global data access and collaboration
- Disaster recovery and business continuity
Cloud Storage Security and Compliance
Security is one of the most critical concerns in cloud storage. Leading cloud providers invest billions in cybersecurity, encryption technologies, and compliance certifications.
Common security features include:
- End-to-end encryption
- Multi-factor authentication
- Role-based access control
- Continuous monitoring and threat detection
Compliance standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, and ISO 27001 make cloud storage suitable for regulated industries like finance, healthcare, and legal services.
Cloud Storage Pricing Models
Cloud storage pricing varies based on usage, performance, and access frequency. Understanding these models helps businesses optimize costs.
- Pay per GB stored
- Data transfer and egress fees
- Tiered storage pricing
- Enterprise subscription plans
High-value enterprise keywords related to cloud storage pricing, cost optimization, and data security attract premium advertisers, contributing to high CPC and eCPM.
Cloud Storage vs Traditional Storage
Traditional on-premise storage requires significant capital expenditure, ongoing maintenance, and physical security. Cloud storage eliminates most of these challenges.
Organizations shifting to cloud storage gain agility, reduce downtime, and improve operational resilience.
Cloud Storage in High-Growth Industries
Cloud storage is foundational in industries that dominate digital advertising spend:
- SaaS and enterprise software
- Financial services and fintech
- Healthcare and telemedicine
- Cybersecurity and data protection
- Media streaming and content platforms
These sectors depend on secure, scalable, and compliant cloud storage solutions to operate globally.
Future of Cloud Storage
The future of cloud storage includes AI-driven data management, automated tiering, predictive analytics, and deeper integration with AI and machine learning platforms.
Innovations such as serverless storage, edge computing, and zero-trust security models will further transform how data is stored and accessed.
Conclusion
Cloud storage is no longer optional—it is a fundamental building block of modern digital ecosystems. Understanding how cloud storage works helps businesses, developers, and decision-makers choose the right solutions for performance, security, and scalability.
As data continues to grow exponentially, cloud storage will remain at the center of innovation, powering the next generation of enterprise applications and digital services.
Comments (3)